
Back to resources
ISO 42001 vs NIST AI RMF 1.0: Building Your AI Governance Strategy
July 2025 / 6 min. read /

As artificial intelligence innovates quickly and adoption continues to skyrocket, so too are expectations around responsible, secure, and ethical AI governance.
There are two leading governance frameworks:
- ISO/IEC 42001:2023 – A certifiable AI management system standard
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework (RMF) 1.0:2023 – A flexible, risk-focused guide for AI development and operation.
Here’s how they compare and how you can strategically implement either (or both) for secure AI adoption.
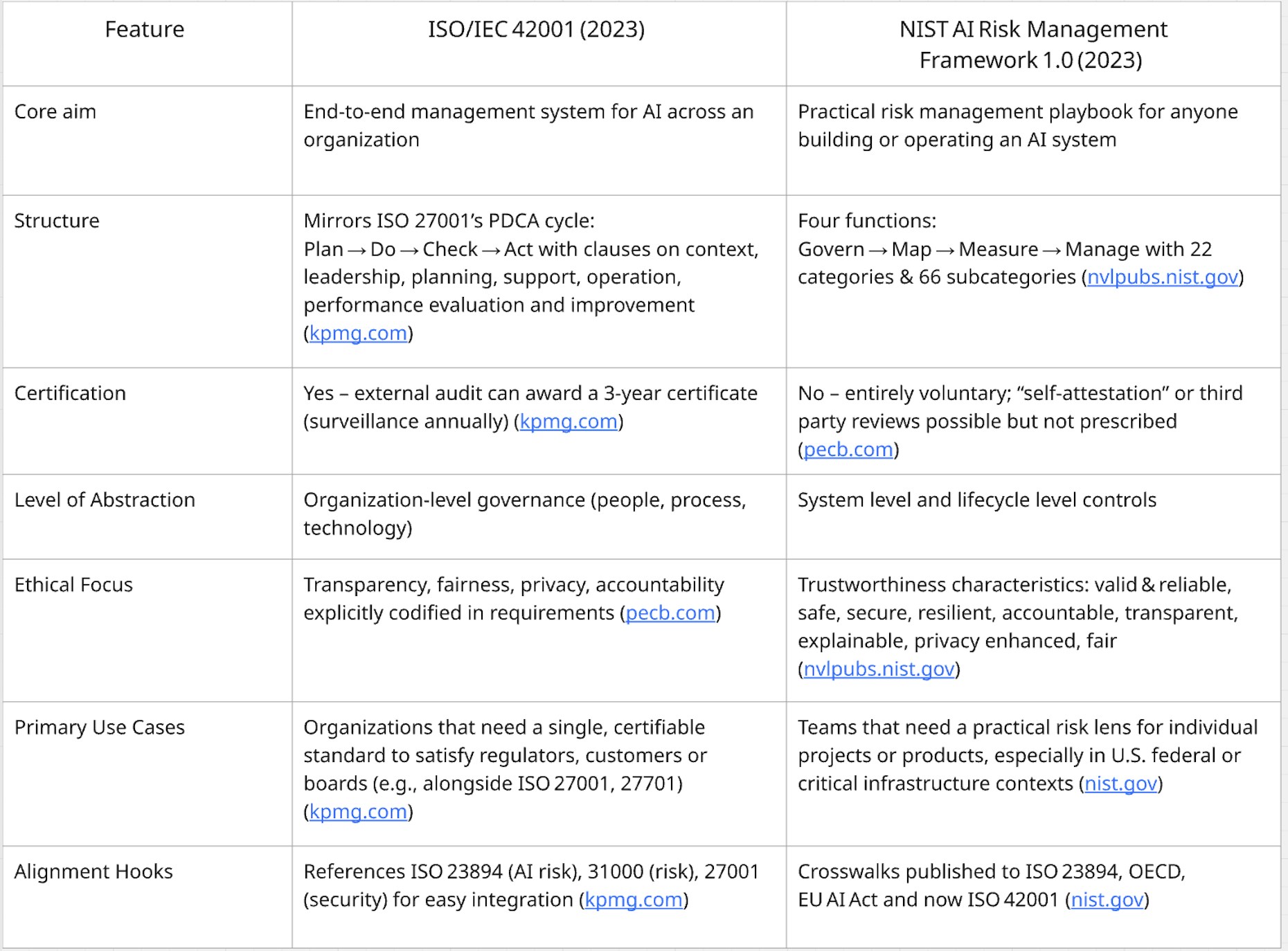
ISO/IEC 42001 and NIST AI RMF 1.0 At-a-Glance
These Frameworks in Practice:
If you’ve used ISO 27001, ISO 42001 will feel familiar: establish an AI Management System (AIMS), define scope, appoint an “AI steering committee,” run risk assessments, set KPIs, and prepare for an external audit. PDCA forces continuous improvement.
If you’ve used NIST CSF, NIST AI RMF is its AI-focused counterpart. You go through the four functions, starting with establishing a governance structure (policies, roles, culture), map your use case and stakeholders, measure risk outcomes and metrics, and manage them through technical and procedural controls. No audit checklists, more lightweight, narrative-driven guides.
Frameworks like ISO 42001 and NIST AI RMF outline the what, but securing AI in practice requires robust, scalable controls at the access layer. Solutions like Britive’s Agentic Identity Security Platform (AISP) can help operationalize these principles by enforcing Zero Standing Privileges (ZSP), providing real-time auditability, and managing just-in-time access for all identities: human, non-human, and agentic AI.
Which One is Right for You?
Need a formal badge on the website or to answer, “Are you certified?” in RFPs (finance, healthcare, EU supply chains)?
- Start with ISO 42001; it gives you a certifiable seal and lines up nicely with existing ISO audit cycles. Then use NIST RMF inside teams as the day-to-day risk playbook.
Moving fast with AI prototyping and want some guardrails, but not clunky governance?
- Use NIST AI RMF first. It’s free, readable, and you can scale up to ISO-levels of control later. Document how each of the four functions is met; this creates evidence if you certify later.
Already ISO 27001/27701 certified or work with auditors familiar with ISO requirements?
- Extending to ISO 42001 is the most efficient path; many clauses can inherit controls from your existing ISMS/PIMS. Layer on NIST functions to show deeper technical coverage.
U.S. federal contractor or critical infrastructure provider?
- Adopt both: federal guidance tends to cite NIST documents, while large customers increasingly ask for an ISO certificate. Use crosswalks to avoid duplicate effort.
Combining Frameworks for the Best of Both Worlds
- Run a gap-analysis first. Map ISO 42001 clauses to the NIST functions (NIST publishes an official crosswalk). This highlights any double-duty artefacts across both frameworks (e.g., risk register, impact assessment templates, etc.).
- Document once, assign evidence twice. Write a single AI policy, then tag each paragraph with the ISO clause and the NIST function it satisfies.
- Leverage existing ISO auditors. Most ISO 27001 certification bodies are gearing up for 42001; the surveillance audits can often be bundled, reducing cost and disruption to your environment.
- Keep the RMF playbook close to engineers. NIST’s checklists (e.g., bias testing, red teaming, etc.) are concrete and help generate the “objective evidence” ISO auditors look for.
- Monitor regulatory drift. The EU AI Act references risk-based governance. ISO 42001 helps prove process conformity, while NIST’s profiles (like the generative AI companion from July 2024) let you adapt and fine-tune controls as new risks emerge.
For technical enforcement of access control policies, especially those tied to runtime privileges, identity verification, and adherence to the principle of least privilege, having a unified policy and platform can standardize how AI agents, developers, and tools interact with sensitive systems.
The Bottom Line
ISO 42001 = a heavyweight, certifiable management‑system standard that signals corporate accountability.
NIST AI RMF = a flexible, technical risk framework that engineers can use immediately.
Most mature organizations will use both: NIST RMF for day-to-day risk work and ISO 42001 as the umbrella that convinces boards, regulators and customers that AI is being governed responsibly.
Supporting an Efficient Dual-Framework Strategy
Securing AI while implementing AI governance through ISO 42001 and NIST AI RMF together requires coordination of policy, processes, and technology across fast-moving teams.
As organizations mature in their AI governance strategies, technology must support, not slow down, compliance and collaboration.
Platforms like Britive help unify access controls across teams, clouds, and AI systems, making it easier to align operational security with both ISO and NIST requirements. That means faster adoption, reduced risk, and controls that evolve as fast as your AI initiatives do.

